Zoonoses
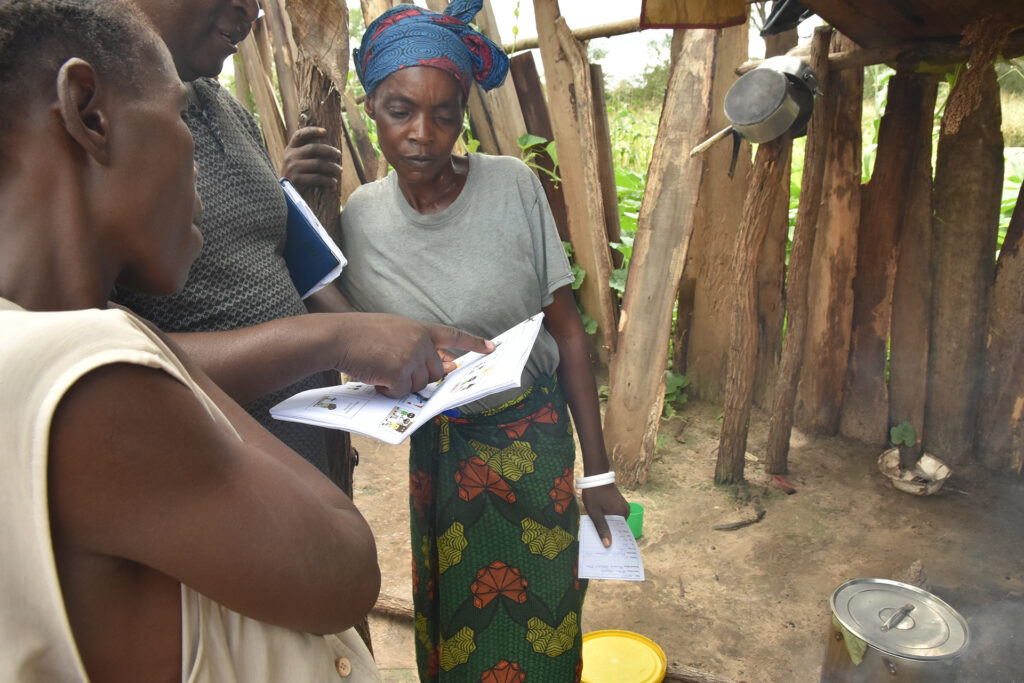
What are the causes and symptoms? Important preventive measures include vaccinations, improving hygiene standards and educating the population. Only through coordinated action by veterinarians, health authorities and municipalities can outbreaks be contained and people and animals protected.
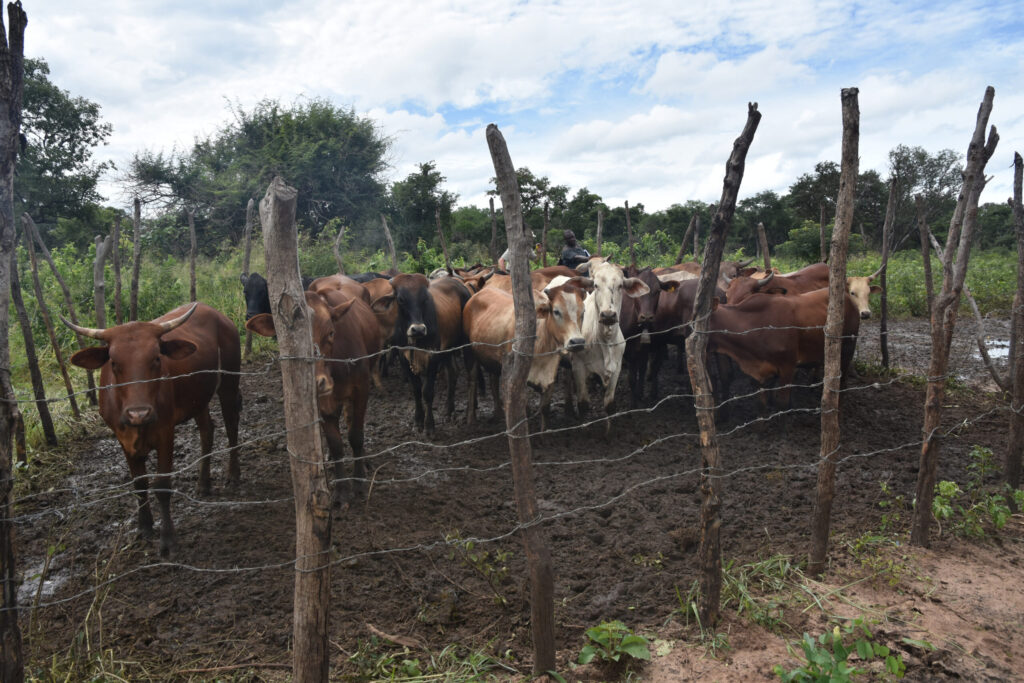

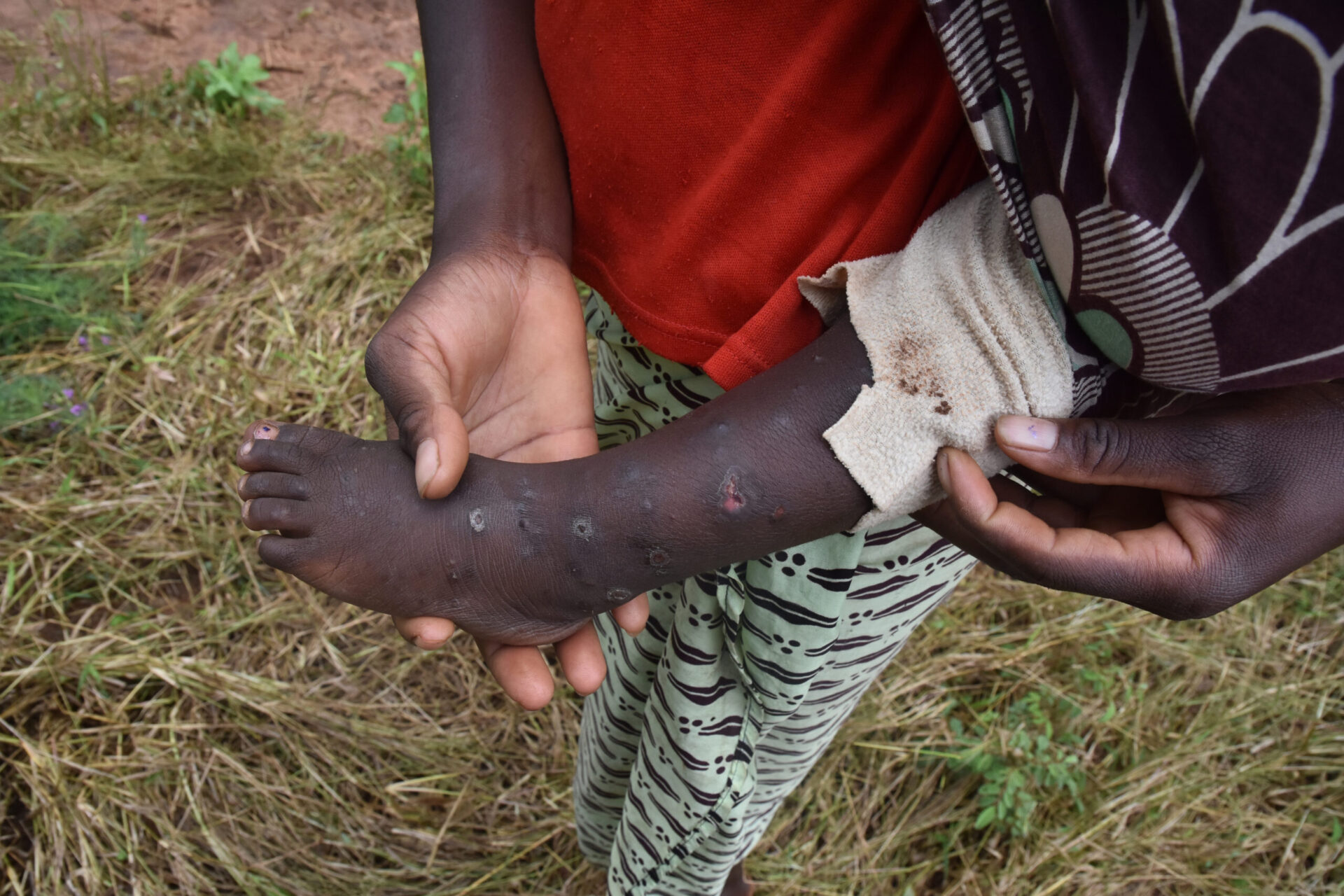
Zoonoses in southern Zambia
In southern Zambia, animal diseases with zoonotic significance are our particular concern. Zoonotic diseases are diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans. Here are some of the zoonotic diseases that occur in the region:
Anthrax:
Anthrax is a rare but serious bacterial infectious disease that can be transmitted from animals to humans. It is caused by the bacterium Bacillus anthracis. Humans can become infected through direct contact with infected animals or their tissue. Anthrax can take various forms, including cutaneous anthrax, pulmonary anthrax and gastrointestinal anthrax. The prevention of anthrax includes measures such as the timely identification and treatment of infected animals, the safe disposal of animal carcasses and raising public awareness of the symptoms and risks of the disease.
Brucellosis:
Brucellosis is a bacterial infectious disease that can be transmitted to humans from animals such as cattle, goats, sheep and pigs. It is caused by various types of bacteria of the genus Brucella. People can become infected by eating raw or insufficiently heated meat or through direct contact with infected animals. Brucellosis can lead to flu-like symptoms, fever, joint pain and long-term complications. The prevention of brucellosis includes the control and monitoring of livestock, the vaccination of animals and the promotion of hygiene measures in food processing.
Rabies:
Rabies is a fatal viral disease that can be transmitted from infected animals, especially dogs, to humans. In rural areas of southern Zambia, where the dog population is high, there is an increased risk of rabies. The vaccination of pets and awareness campaigns about the risks of rabies play an important role in combating this disease.
Bovine tuberculosis:
Bovine tuberculosis is a bacterial infectious disease that can be transmitted from cattle to humans. It is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium bovis. Humans can become infected by consuming unpasteurized milk or through direct contact with infected animal tissue. The disease can have serious health effects, including pneumonia and tuberculosis. The control of bovine tuberculosis requires comprehensive screening and testing programs for cattle herds and the promotion of hygienic milk processing practices.
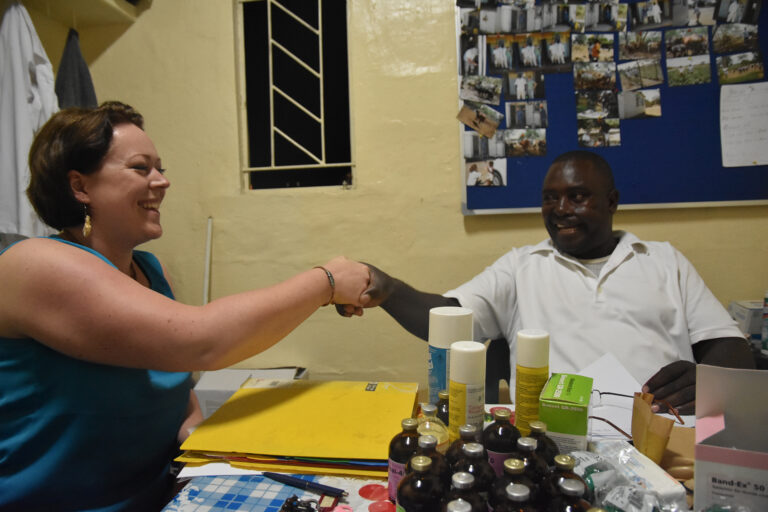


Conclusion:
Combating these diseases requires close cooperation, vaccination and education. We have carried out important educational campaigns to raise awareness of the risks and preventive measures. Adherence to good agricultural practices and hygiene standards and the implementation of vaccination programs help to contain the spread of these zoonotic diseases and protect both animal and public health. This is why Zambesi Health repeatedly finances vaccination campaigns.
Become a member now
Become a member of our association and support innovative development cooperation! Together we can bring about real change.

